Research progress on the interfacial properties of polyester fiber/TPU coated fabrics
Research progress on the interfacial properties of polyester fiber/TPU coated fabric
Polyester fiber/TPU coated fabric is a composite material with polyester fiber as the base and TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane) as the coating. Because of its series of advantages such as light weight, high strength, hygiene, and environmental protection, it is widely used in sportswear, raincoats, leather It is widely used in rowing boats, tents, soft water storage, oil storage containers and other fields [1~3]. ‘Polyester fiber is a synthetic fiber with large output and excellent performance. It has high strength, high modulus, excellent thermal stability and aging resistance, as well as good resistance to organic solvents, oxidants and corrosion resistance [4.51. However, due to the symmetrical molecular structure of polyester, high crystallinity, and lack of highly polar groups in the structure, its hydrophilicity is very poor, and its moisture regain is only. 4%, which brings difficulties to the coating (lamination) of polyester fiber. Interface modification is an effective measure to improve the coating properties of polyester fiber and improve the composite fastness of the coated fabric interface. Since its coating material TPU contains certain polar groups [1], the surface modification of polyester fiber has become the focus of research on the interface modification of the coated fabric. Based on the analysis of factors affecting the polyester fiber/TPU coated fabric interface, this article reviews the current polyester fiber surface modification treatment and coated fabric interface research methods, and briefly analyzes their advantages and disadvantages. 1 Analysis of factors affecting the interface of coated fabrics From the perspective of the formation process of the polyester fiber/TPU coated fabric interface, the factors affecting the interface of coated fabrics mainly include the quality of the coated fabric, polyester fiber textile printing and dyeing, and the coating preparation process. Among them The coated fabric matrix is the fundamental factor affecting its interfacial bonding.
1.1 Coated fabric substrate
The matrix composition of polyester fiber/TPU coated fabric mainly includes polyester fiber and TPU. Polyester fiber is made from purified terephthalic acid (m~) or dimethyl terephthalate (DMT) and ethylene glycol (EG) as raw materials through esterification or transesterification and polycondensation reaction. The polymer polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a fiber made by spinning and post-processing. Its molecular formula is [-OC—C6H. —COOCH:CH:o]. . Due to the symmetrical molecular structure of polyester, its high degree of crystallinity, and the lack of highly polar groups in its composition, it is difficult for polyester fiber to achieve good interfacial bonding as a coated fabric base fabric. Its coating material is TPU, and its general molecular formula is [-R, NHCOOR2-]. , due to the existence of _NH-, -C00- active groups in its molecular structure, it provides the possibility of good interfacial bonding of coated fabrics. In summary, the inert surface of polyester fiber in the matrix composition of polyester fiber/TPU coated fabric is the bottleneck restricting the interfacial bonding of the coated fabric. Therefore, surface activation modification of polyester fiber is the key to improving the interfacial bonding of the coated fabric. . Polyester fiber spinning, printing and dyeing Polyester fiber will eventually become a coated fabric base fabric through the spinning, printing and dyeing process. The spinning, printing and dyeing process will inevitably be accompanied by sizing and oil stains, and the incomplete removal of sizing and oil stains will reduce the infiltration of the fabric. The properties and permeability directly affect the interface bonding of coated fabrics, so the cleaning of polyester fabrics after printing and dyeing is particularly important. In addition, the production process of polyester fiber will be accompanied by the production of oligomer by-products. Among them, cyclic oligomers have low water solubility, which will cause problems in the dyeing process and coating preparation process. Research shows that when the temperature is higher than 130°C, the mobility of polyester long molecular chains intensifies, and cyclic oligomers accumulate on the fiber surface. Therefore, controlling the temperature of printing and dyeing and related processes at around 100°C is important for obtaining interfacial bonding. A good coated fabric is also important.
1.3 Coating preparation process
The coating preparation process is the basis for forming the fiber/coating interface. Therefore, when the fiber and coating are given, the process control of the coating preparation process is the key to the formation of the polyester fiber/TPU coated fabric interface and obtaining good interface bonding. Coating thickness is one of the important properties of coated fabrics, which directly affects the interface bonding strength and performance of coated fabrics. As the base fabric of the skeleton material, the existence of the cloth pattern causes the actual surface to be uneven. When the coating is too thin, it is not enough to fill the grooves of the cloth pattern, making the coating discontinuous and prone to leakage; the coating is too thin Thickness will not only increase the weight of the coated fabric, but also increase the product cost. Therefore, the actual thickness of the coating should be reasonably controlled according to its actual application situation to ensure that it is as “high quality and low price” as possible while meeting the performance. The coating preparation temperature is also an important factor affecting the interfacial bonding of coated fabrics. Studies have shown [7| that as the coating preparation temperature increases, the composite film composite fastness of coated fabrics increases significantly. This is because increasing the coating preparation temperature, on the one hand, accelerates the fusion of the coating material and the base fabric, and improves the mechanical bonding of the coated fabric interface; on the other hand, the increase in temperature helps the polymer molecules to bind at the coated fabric interface. Diffusion between them forms a strong and lasting chemical bond. However, the coating preparation temperature should not be too high, otherwise it will increase the difficulty of process control, increase process costs, and also cause a loss of strength of the polyester fiber. 2 Polyester fiber surface modification is a very practical and effective technical measure to improve the peel strength of coated fabrics by changing the surface state of the base fabric. At present, the main methods used for interface treatment of polyester fiber/n)U coated fabrics include alkali treatment, corona discharge and plasma treatment, dipping treatment, etc.
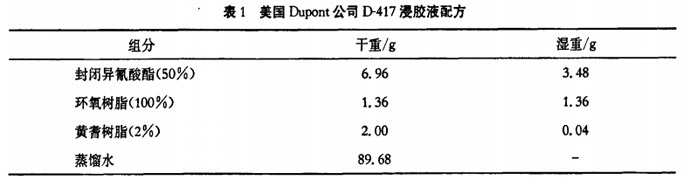
<img src="https://www.alltextile.cn/Uploads/image/20190216/20190The mechanical interlocking force between coating and fabric is also greater. Due to the inert surface of polyester fiber and poor hydrophilicity, there are only a small number of carboxyl and hydroxyl groups at the ends of the polyester molecular chain, so the contribution of van der Waals forces is not significant. Through the reaction between the dipping solution and the polyester fiber, active groups such as hydroxyl groups are introduced on the surface of the polyester fiber to form a chemical bond between the fabric and the coating. The resulting chemical bond force has a great influence on the interfacial bonding of the coated fabric. Taking the formula of D-417 dipping solution as an example, the reaction mechanism between the dipping solution and polyester fiber is that the reaction between the epoxy group of the epoxy resin and the terminal carboxyl group of the polyester introduces active monoOH, blocking the isocyanate at high temperature The NCO group is unblocked to produce a highly active NCO group, and the NCC polyester reacts with an OH group or is re-esterified directly. At high temperatures, there is also a reaction between isocyanate and polar esters in polyester, and a cross-linking and curing reaction between isocyanate and epoxy resin. Through the reaction, highly active mono-OH and mono-NH are introduced into the polyester molecules, and in A resin-like coating is formed on the surface of the polyester fiber, which enhances the polarity of the polyester and strengthens the chemical bonding between the polyester and the coating material. Interface research methods Interface research has always been a focus and difficulty in the field of composite materials research. For coated fabrics, due to the irregularity of the fiber surface and the lack of rigidity of the fiber itself, coupled with the porous structure of the fabric surface, the application of some traditional interface characterization methods is limited. , its interface research method is more difficult. Interface research methods are mainly divided into the following four aspects: fabric wettability characterization, fabric surface morphology characterization, interface reaction dynamic process characterization, and interface bonding force characterization.
3.1 Characterization of fabric wettability
The wettability characteristics of fabrics mainly include surface tension, contact angle, wetting time, etc. Use a surface tension meter to characterize the surface tension changes of the fabric before and after treatment, so as to make a qualitative judgment on the treatment effect. Wetting time is also a good parameter to characterize the wettability of fabrics. The principle is to drop test droplets of deionized water onto the fabric surface respectively, observe the state of the droplets at different time points, and test the requirements for complete spreading on the fabric surface. time question. It is difficult to test the static contact angle of fiber. The CahnBalance method is generally used to measure the dynamic contact angle of liquid on the fiber surface. The test principle is to hang the straight fiber vertically on the hook at one end of the electronic balancer, and at the same time, a liquid is placed in a The beaker is placed on a liftable platform. When the liquid rises, the suspended fibers contact the liquid at a constant speed, and the fibers are moistened by the liquid; when the liquid falls, the fibers are dewetted. The force experienced by the fiber during wetting and dewetting is different. Based on this, the dynamic contact angle of the liquid on the fiber can be measured, as shown in formula (1). cos0=F/(), ·7r·d) (1) in the formula, where is the contact angle of the liquid on the fiber surface, F is the force on the fiber during the wetting or dewetting process, y is the surface energy of the liquid, d is the diameter of the fiber.
3.2 Characterization of fabric surface morphology
Although alkali treatment, corona discharge, plasma treatment and dipping treatment have little effect on the surface morphology of polyester fibers, with the help of advanced instrumental analysis methods, changes in fiber surface morphology before and after treatment, especially roughness, can still be observed. degree of change. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) and atomic force microscope (AFM) are relatively common means of analyzing the micromorphology of non-metallic materials. The resolution of SEM electron microscope can reach 3 nanometers, and the resolution of AFM microscope can reach 300 nanometers, which is exactly the same as plasma treatment. The scope of action is basically the same and can well reproduce the changes in fiber surface morphology and roughness before and after treatment
3.3 Characterization of dynamic process of interface reaction
In order to obtain quantitative information on the chemical composition of the polyester fiber surface before and after treatment, advanced analytical testing methods such as X-ray electron spectroscopy and scanning electrochemical microscopy can be used to quantitatively analyze the binding components and binding states of the polyester fiber surface atoms, and then infer the treatment process. Chemical effects and reaction processes on polyester fiber surface elements and components.
3.4 Characterization of interface bonding force
A direct and effective way to judge the effectiveness of the interface treatment of coated fabrics is to test the interface bonding strength of coated fabrics, such as the H extraction force value used to characterize the interface bonding strength of tire cords, the peel strength of coated fabrics, etc.
Conclusion
Based on the study of factors affecting the interface of coated fabrics, this paper analyzes and concludes that the surface inertness of polyester fiber is the bottleneck that affects the formation of good interfacial bonding of coated fabrics, and the surface modification of polyester fiber is an effective measure for coated fabrics to obtain good interfacial bonding. . Alkali solution treatment, corona discharge and plasma treatment have limited effect on the surface activation of polyester fiber, and the main application focuses on polyester fiber printing and dyeing; dipping treatment is an important technical measure for surface activation of polyester fiber and improvement of the interface bonding of coated fabrics. , based on the commonly used dipping solution formula, the mechanism of activated polyester fiber by dipping treatment was briefly analyzed. In the research of coated fabrics, the lack of depth and breadth of interface research methods is the main reason for the slow progress of coated fabric research. With the application of advanced instruments such as X-ray electron spectroscopy, scanning electrochemical microscopy, and dynamic contact angle measurement instruments, The emergence of detection instruments will greatly promote the interface research of coated fabrics. At the same time, the research on fiber-reinforced metal-based, resin-based, and ceramic-based composite materials has certain reference significance for the research on the interface of coated fabrics and the improvement of interface bonding. sdafwfetghe
Disclaimer:
Disclaimer: Some of the texts, pictures, audios, and videos of some articles published on this site are from the Internet and do not represent the views of this site. The copyrights belong to the original authors. If you find that the information reproduced on this website infringes upon your rights, please contact us and we will change or delete it as soon as possible.
AAAafwfetghe
Disclaimer:
Disclaimer: Some of the texts, pictures, audios, and videos of some articles published on this site are from the Internet and do not represent the views of this site. The copyrights belong to the original authors. If you find that the information reproduced on this website infringes upon your rights, please contact us and we will change or delete it as soon as possible.
AA







