Function and testing of UV-resistant textiles
Function and testing of UV-resistant textiles
UV protection (UVprotection) – UV performance is generally evaluated using the UPF value, which is the ultraviolet protection factor value. The UPF value is the ratio of the average amount of ultraviolet radiation to unprotected skin
UV protection
With the development of modern industry, the ozone layer in the atmosphere is constantly being destroyed, resulting in a significant increase in ultraviolet radiation on the surface. Ultraviolet rays refer to the electromagnetic waves emitted by the sun with a wavelength of 200-400nm. It can cause severe damage to human skin. The UVA and UVB bands will promote the production of melanin, cause cortical aging, and even cause cataracts, skin cancer and other lesions. Anti-UV has now become a self-protection behavior that people are accustomed to. There are endless sunscreen products in daily life, such as sunscreen, umbrellas, sunglasses, etc., all of which are marked with the UPFXX logo. In outdoor activities, especially mountaineering and other activities, due to the relatively high altitude of the mountains, the ultraviolet radiation is much stronger than on the flat ground. At this time, clothing is a direct shield for people to resist ultraviolet radiation, so the anti-ultraviolet performance of the fabric is extremely important. It’s important.
The ability of fabrics to protect against ultraviolet rays mainly depends on the ability of the fabric itself to shield ultraviolet rays. Fabrics usually have relatively complex surfaces. In addition to absorbing light, they also scatter and reflect light. The effect of transmitted ultraviolet rays on the skin is Under normal circumstances, as the absorptivity and reflectivity increase, the transmittance decreases, and the protective performance is superior.
There are currently several international testing standards for the UV resistance of fabrics, such as AATCC183/AS/NZS4399-1996/EN13758, etc. They all simulate the wavelength of ultraviolet light (UVA280-400). After irradiating the fabric multiple times, Analyze its numerical values and calculate its ultraviolet transmittance, shielding rate, absorption rate and UPF value. The factors that affect the UV radiation resistance of fabrics are: fabric structure, fabric color, and processes such as bleaching and dyeing. Through testing, we found that the tighter the woven or knitted structure, the greater the UPF value. When taking a piece of light-colored fabric and a piece of dark-colored fabric with the same texture and structure, and conducting a UV irradiation test at the same time, it can be found that the dyed fabric has a higher UPF value than the undyed fabric, and the darker the fabric, the more UV rays are transmitted through it. The smaller the rate, the higher the UV protection ability. The UVR absorption performance of the fabric depends on the processing methods used in the weaving process, such as bleaching, dyeing, applying matting agents, etc. These processing processes will have an impact on the UVR absorption performance of the fabric. The general rules for the anti-UV radiation performance of fabrics are: short fibers are better than filament fibers, processed silk products are better than raw silk products, fine fiber fabrics are better than coarse fiber fabrics, flat special-shaped fabrics are better than circular cross-section fabrics, and woven fabrics are better than knitted fabrics.
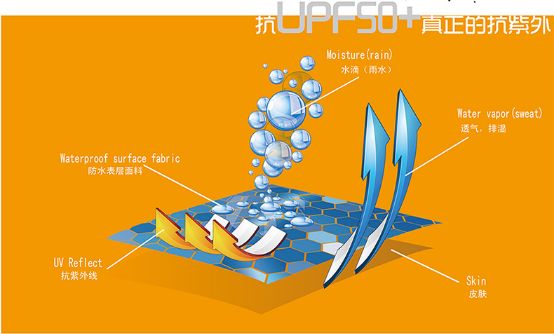
In order for the fabric to obtain better UV protection properties, the finishing of the fabric is also very important. The processing of UV protection fabrics mainly uses various methods to treat fibers, yarns or fabrics with inorganic and organic UV finishing agents separately or together. And make it firmly bonded, in addition to the traditional finishing method or coating method, high-tech nano-spinning technology is used to add an ultraviolet isolation factor (nano-titanium oxide Ti02) during the slicing polymerization process to make the fiber and its The product can effectively absorb ultraviolet rays, prevent ultraviolet rays from penetrating through clothes, and protect the human body from various skin diseases caused by excessive ultraviolet rays. At the same time, it can reflect visible light and infrared rays, reduce the temperature rise caused by solar thermal radiation, and keep the inside of clothes The cool feeling makes wearing more comfortable and safe. It has the characteristics of long-lasting anti-ultraviolet effect and never fades. No matter what washing method is used, and how many times it is washed and dried, it has no effect on the anti-UV function of fibers and fabrics.
In summer or in plateau areas, many friends wear clothing with anti-UV fabrics when traveling. So how do these so-called anti-UV fabrics prevent or stop the harm of ultraviolet rays in the sun to the human body? Below I will briefly introduce the performance and common sense of some UV-resistant fabrics for your reference and discussion together.
We all know that sunlight includes visible light, ultraviolet (UV), infrared and other light bands, among which the light with a wavelength of 100-400 nanometers is ultraviolet (the ultraviolet spectrum is divided into three bands: UVA, UVB, and UVC, among which UVA and UVB It is very harmful to the human body. To put it simply, UVA tans you and causes a large amount of melanin to deposit in the epidermis. UVB can penetrate the epidermis and long-term exposure can cause genetic factor DNA damage and lead to skin cancer), which accounts for 6.1 of the sun’s rays. %. The harm of ultraviolet radiation to the human body has attracted more and more attention. Ultraviolet rays can cause sunburn, aging, and the production of melanin and spots on human skin. In more serious cases, it can also induce cancer in the human body. In terms of clothing fabrics, ultraviolet rays can accelerate the fading and brittleness of textiles. Now some European countries have legislated to require the use of anti-ultraviolet fabrics in clothing uniformly made for students. my country has also formulated its own corresponding anti-ultraviolet standards for textiles. It should be said that As people’s awareness of health continues to increase, textiles with UV protection functions have become more and more popular.It has attracted everyone’s attention.
The principle of UV protection fabrics:
The principle of anti-UV fabric is to use the ultraviolet absorber mixed into the fabric to absorb high-energy ultraviolet rays and convert them into low-energy heat energy or electromagnetic waves with shorter wavelengths, thereby eliminating the harm of ultraviolet rays to the human body and fabrics. The use of ultraviolet reflectors can increase the reflection and scattering of ultraviolet rays by fabrics and prevent them from penetrating the fabric. It has the properties of heatstroke prevention, heat insulation and cool touch.
It should be noted that national standards stipulate that fabrics with UPF5% cannot be called anti-UV fabric products.
The unit of ultraviolet sun protection is the UPF value. The method for calculating the UV protection function is; UPF = the small amount of exposure that produces erythema when the skin is not protected/the small amount of exposure that produces erythema when the skin is protected, that is, when you wear this dress, you Can withstand several times the sun exposure time.
Anti-UV clothing fabrics include cotton, linen, silk, wool, chemical fiber and other fabrics. Some anti-UV fabrics that have been processed by better processes have good absorption of ultraviolet rays in the 180-400nm band (especially UV-A and UV-B). Through conversion, reflection and scattering, the finished fabric is non-toxic, non-irritating to the skin, and the human body will not produce allergic reactions. At the same time, it does not affect the coloration and moisture absorption and breathability of the fabric. Good anti-UV fabrics have good absorption effects on ultraviolet rays in the 100-400cm band, especially UV-A and UV-B. After 50 washes, the ultraviolet transmittance is still less than 1%, and the ultraviolet blocking factor UPF can reach 50 +High level.
Differences in UV protection properties of different fabrics:
Among various clothing fabrics, thicker fabrics have better UV resistance than thin ones. Among them, polyester fiber has better UV resistance, which is related to the benzene ring in the molecular structure of polyester fiber that absorbs ultraviolet rays. The UV resistance of nylon, cotton, and silk is not satisfactory. Therefore, when choosing anti-UV clothing, you should try to choose thick fabrics containing polyester fibers. (The UV protection performance of some domestic polyester fiber fabrics has now reached a very high level).
The tighter the fabric, the stronger its light-blocking ability and the less UV rays it transmits. Woven fabrics have better UV protection than knitted fabrics. The darker the color of the clothing fabric, the smaller the UV transmittance and the better the UV protection performance.
Two types of anti-UV finishing processes for clothing fabrics:
1. Use ultraviolet absorbers to post-process the fabric to achieve ultraviolet protection.
2. Use ceramic micropowder to combine with fibers to increase the reflection and scattering of ultraviolet rays on the surface to prevent ultraviolet rays from penetrating the fabric and damaging human skin.
What is UPF
A note on UPF value
UPF is the abbreviation of English Ultraviolet Protection Factor, which is ultraviolet protection factor.
According to the definition in the national standard, UPF refers to “the ratio of the average effect of ultraviolet radiation calculated when the skin is unprotected to the average effect of ultraviolet radiation calculated when the skin is protected by fabrics.”
This definition is relatively abstract. We can understand the physical meaning of UPF in this way. For example, a UPF value of 50 means that 1/50 of the ultraviolet rays can penetrate the fabric.
The higher the UPF value, the better the UV protection effect. However, the national standard for textiles with high UPF value is 50+, that is, UPF>50. Because after UPF is greater than 50, the impact on the human body is completely negligible.
The “Evaluation of UV Protection Performance of Textiles” standard promulgated by the General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine stipulates:
A. Only when the UPF value of the sample is greater than 30 and the transmittance of UVA is less than 5%, can it be called an “UV-resistant product”. These two conditions are indispensable. This is a constant indicator of whether a product is a “UV protection product”.
B. UV protection products should have three aspects on the label:
1. National standard number: GB/T188302
2. UPF value:
3. 30+, or 50+
Remarks:
If the measured UPF value is greater than 30 and the UVA transmittance is less than 5%, the mark is: 30+
If the measured UPF value is greater than 50 and the UVA transmittance is less than 5%, the mark is: 50+3
The protective properties provided by this product may be reduced with long-term use, stretching or moisture C7Qau6
Disclaimer:
Disclaimer: Some of the texts, pictures, audios, and videos of some articles published on this site are from the Internet and do not represent the views of this site. The copyrights belong to the original authors. If you find that the information reproduced on this website infringes upon your rights, please contact us and we will change or delete it as soon as possible.
AA







