Principles and methods of waterproof and breathable coating
Principles and methods of waterproof and breathable coating
After coating, textiles can not only change their appearance, but also be given various functions according to people’s requirements to be suitable for different uses. Coating finishing is an important means for deep processing of textiles. The coating centered on waterproofing and moisture permeability is a new technology that has been studied at home and abroad. In foreign countries, in the 1970s, the American Gore Company’s Gore-rex polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) waterproof and permeable membrane was successfully researched. Japan also manufactured Miero-tex polyurethane waterproof and breathable membrane in the early 1980s. The DicrylanPC water-dispersed microporous acrylate coating agent of Ruib Ciba-eigy]/_~ Company and the Imprani1DLN water-dispersed microporous polyurethane coating agent of Bayer Company of West Germany are both products with excellent waterproof and breathable properties. Rain farmers, jackets, skis and sportswear sewn with waterproof and breathable coating fabrics. Because rainwater cannot penetrate, the sweat vapor in the body can be emitted, making the garment very comfortable, and it is a popular mid-to-high-end product in the international market. Our factory cooperates with Shanghai Textile Research Institute to conduct research, which fills the gap in our waterproof and breathable coating products.
2. Principles and methods of waterproofing and moisture permeability
(-) Waterproof and breathable coating principle
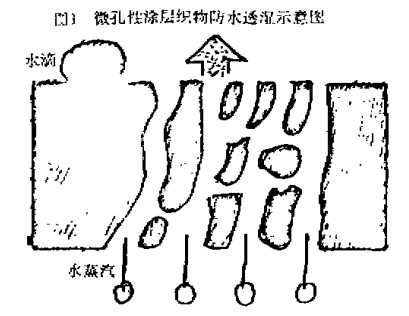
After the original transparent fabric is waterproofed, it becomes a continuous film, which seals the gaps in the yarn and reduces the moisture content, or even makes it less wet. To make the fabric permeable, it is necessary to change the continuous film of the coating into a mesh structure film with countless holes. This kind of micropores can form a channel in the gaps between the fabric yarns; There should be a certain water vapor difference in the material, and the air will diffuse on the other side of the channel. The microporous structure is small, only 0.5-20u, and the diameter of the water droplets is large, in the range of l00. ;0a reading, so raindrops cannot pass through. The diameter of water vapor (sweat) is only 0.0004;~, so it can escape in large quantities, achieving a waterproof and moisture-permeable effect.
(2) Waterproof and breathable methods
From the perspective of coating, there are dry and wet methods for temperature penetration: from the perspective of properties, there are physical and chemical methods; from the method itself, there are forging holes method and mechanical foaming method. Membrane method, chemical group method and microfiber dense fabric method. The method itself is described as follows:
1. Microporous moisture permeability method
The formation of microporous remote-wetting coatings mainly relies on adding volatile ethyl acetate, perchlorethylene, self-fired oil and easily soluble dimethylformamide (DMF) and methylcellulose cord ( CMC) and other substances, volatilize or dissolve during heat treatment or water washing, forming a film with a microporous network structure (Figure 1, circle 1). This moisture-permeable method is suitable for micropores. The moisture permeability of the dry-joined coating of a microporous coating agent depends on the quality and application process of the porous coating agent. The moisture permeability of the microporous coating is the lowest among several methods, and the synthesis process is relatively simple. It is easy to implement, low in cost and convenient to operate. The diameter of the pores is generally between 0.5 and 2 mm, and the microporosity is about 80%.
2. Mechanical foaming and moisture permeability method
The formation of micropores in this method is mainly through mechanical foaming. Add fillers, cross-linking agents, stabilizers and foaming agents to the coating agent, use a machine to generate foam, and then apply it to the fabric. After drying, it is rolled to break the bubbles and form micropores. This is a stable foam that will not burst naturally after being left for a week. It is different from the mechanical foaming of foam finishing, which is broken after drying and is a metastable foam (Froth). This method is suitable for mechanical foaming and crushing after rolling. Its moisture permeability depends on the foaming quality. The moisture permeability is acceptable, but the process operation is troublesome. It requires a foaming machine and a reciprocating application device. The micropore diameter is between 5 and 10^1.
3Thin film moisture permeability method
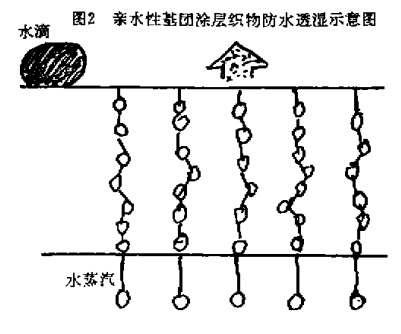
This method first makes a microporous film and then composites it with the fabric. PTFE microporous film is produced using special processing methods. It is first formed into highly crystalline particles, and then under high temperature conditions of 390-400°C, uniform pulling force is given in both vertical and horizontal directions at the same time, and it is quickly stretched into a film. The thickness is 20-25m, the diameter of the micropores is as large as 0.2u, and the pore density reaches 1.395 billion/cm. The polyurethane microporous structure film is also manufactured using the above-mentioned similar principles, with a micropore diameter of 0_u and a pore density of about 155 million/cmt. This method is suitable for laminating composite coating films on textiles. Its moisture permeability depends on the quality of the film. It has high moisture permeability and high waterproof performance. However, the technical difficulty and cost of manufacturing the film are quite high. 4. Chemical moisture permeability method with highly hydrophilic groups. This is a non-microporous film material. The key feature of this moisture-permeable water drop circle 2 hydrophilic group-coated fabric waterproof and moisture-permeable schematic coating is that it contains a sufficient amount of highly hydrophilic groups in the polyurethane macromolecular structure to act as a ladder for water vapor to move. Water vapor penetrates the film through physical effects such as absorption, diffusion, and desorption.
This method is suitable for composite coatings. Its moisture permeability depends on the number of hydrophilic groups. Its moisture permeability is high, 50 times higher than that of microporous structure
Disclaimer:
Disclaimer: Some of the text, pictures, audio and video of some articles published on this site come from the Internet and do not represent��Website views, the copyright of which belongs to the original author. If you find that the information reproduced on this website infringes upon your rights, please contact us and we will change or delete it as soon as possible.
AA







