In the dyeing and finishing process of pure cotton knitted fabrics, after the fabrics are dyed, fixed and softened, they often need to be repaired due to dyeing defects. Before the fabric is repaired, it needs to be solidified, siliconed, and even stripped.
Sometimes after solid removal, silicon removal, and cleaning, if you encounter partial chromatic aberration or shading For deviations in color change, etc., it is necessary to add dyes and counter-dyes; sometimes after solid removal, silicon removal and color stripping, if there are deviations in color, flowers and stains, etc., it needs to be re-dyed.
For fabrics with downward bias and color deviation that have not been fixed and softened, it is generally easier to repair and re-dye them. After color and soft finishing, especially pure cotton knitted fabrics after baking or heat setting, the difficulty of repairing is greatly increased.
Characteristics of fixing agents and softening agents
1. Fixing agent Color agents
In order to improve the color fastness of pure cotton fabrics to soaping, the fabrics need to be fixed and finished after dyeing, especially deep-colored fabrics dyed with direct dyes and reactive dyes.
The fixing agents currently used are basically formaldehyde-free cationic fixing agents, which have stable performance in weak acid baths and can combine with dyes through ionic bonds to form insoluble lake deposits. On the fiber, it reduces its water solubility and improves the soaping color fastness of the fabric.
If the fixing agent remaining on the fiber and its products with the dye are not fully removed before repair, the dye will be dyed very quickly during counter-dying. If the dye transfer property is poor, it will inevitably lead to color flowers and stains. Even adding a leveling agent will not help. If the dyed fabric is baked, the color flowers and stains will become more serious.
2. Softeners
Softeners can be divided into cationic types , anionic, nonionic and amphoteric. Among them, amino silicone oil cationic softeners have excellent lubrication effects. They mainly generate elastic network structure polymers on the fiber surface through self-crosslinking and condensation, which can give the fabric a soft feel and high washability. However, if the dyeing fastness needs to be repaired, it will be more difficult to re-dye.
At present, the silicone softeners on the market mainly include amino polysiloxane, epoxy polysiloxane, polyether polysiloxane, and polyether epoxy polysiloxane. Oxane and polyether aminopolysiloxane, etc. If it is a fatty acid derivative softener, it can be removed from the fabric by washing with hot water or adding a small amount of alkali.
Repair process and process parameters
1. Process flow
Enter the tank → wash with hot water (80℃×10 rain) → wash with overflow water (10 min) → remove solids and silicon → wash with overflow water (10 min) → strip the color , solid removal, silicon removal → bath → overflow washing (10 min) → clean washing → overflow washing (10 min) → oxygen bleaching → overflow washing (10 min) → chlorine bleaching → dechlorination → overflow washing (10 rain)→secondary dechlorination→overflow water washing (20 min)→hot water washing (80℃×10 min)→counterstaining
2. Process parameters
2.1 Entering the cylinder
During repair, the fabric needs to be in the dyeing machine for a long time In order to reduce the wear and tear of the fabric, the weft-knitted cotton knitted fabric should be turned over and loaded into the pot with the back of the fabric facing outward.
2.2 Solid removal and silicon removal
(1) Solid removal , silicone removal prescription/(g/L)
( 2) Heating curve of solid removal and silicon removal
The solid removal agent is a special polymer Polymer is a non-ionic strong dispersant that can effectively remove the color-fixing agent on pure cotton fabrics and break the ionic bond formed between the cationic group in the color-fixing agent molecule and the anionic group of the anionic dye. Fully remove the color-fixing agent on the fiber and the reaction products with the dye. Therefore, the solid remover itself also has a certain color stripping effect. Silicone remover has high emulsification and foaming properties, and has outstanding decontamination ability. It can effectively destroy the chemical bonds formed by the amino groups in the amino silicone softener and the hydroxyl and carboxyl groups on the cellulose fibers.
In addition to having a certain color stripping effect, soda ash can mainly remove oil on fabrics and reduce the staining of fabrics by stripped softener residues. When the temperature is lowered to 80°C after each process, the liquid is not drained directly, but is washed with overflow water to 30°C and then drained. This is because most of the stripped softener residue and oil are floating in the working fluid foam and need to be effectively removed by overflow water washing. Chelating dispersants can chelate metal ions, soften water quality, and correspondingly improve the effects of solid removers and color-correcting silicone removers.
2.3 One-bath method of color stripping, solid removal and silicon removal
(1) One-bath recipe for color stripping, solid removal and silicon removal/(g/L)
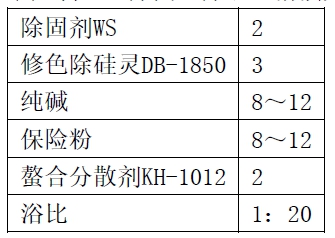
(2) One-bath temperature rise curve for color stripping, solid removal and silicon removal
Commonlyusedstrippingagentsincludereducingagents,oxidizingagents,anddetergents.��Powerfulsurfactantsandalkalis,etc.
Amongthem,themosteffectiveadditiveisthereducingagentsodiumdithionite(insurancepowder).Ithasstrongcolorstrippingabilityunderalkalineconditions,candestroythechromogenicgroupofthedye,makethecolorofthefiberdisappearcompletelyormostly,andcanalsodestroythefixingagent.Insurancepowderisunstableinaqueoussolutionandeasilydecomposesintosulfurdioxideandreleasesalotofheat.Whenthetemperatureisraisedto80°C,insurancepowderisaddedcyclicallytopreventpartoftheinsurancepowderfromdecomposingandfailingduringtheheatingprocess.
Carryoutsiliconeandsolidremovaltreatmentbeforestripping,whichcanremovethesoftener,solidremoverandsomeresidualsubstancesonthefibersurfacethathavenotchemicallyreactedwiththefiber.
Whenstripping,useonebathofcolorstripping,secondarysolidremoval,andsiliconremovaltomaximizetheremovalofcolorfixingagents,softenersandtheircombinationsonthesurfaceandinsideofthefiber.Productsandresiduesoffiberreactions.
Beforestripping,asolidandsiliconremovaltreatmentat100°CWhenstaining,theunreactedsofteneronthefabricwillbreakemulsions,bleachoil,andformadarkbrownstickypaste,causingsecondarystainingofthefabric.Forfabricsthatdonotrequirecolorstrippingsuchasdownwardchromaticaberrationandchromaticlightdeviationdiscoloration,theheatingcurvelistedinthissectioncanbecarriedoutaccordingtothesolidandsiliconremovalprescription,andthetemperaturecanbequicklyraisedto130°C×40minutes;fordeepanddensecolorsForfabricswithseriousstainsandflowers,thedosageofinsurancepowderandsodaashcanbeincreasedto12g/Lwhenstripping.
2.4Cleansing
(1)Cleansingprescription/(g/L)
( 2) Cleaning temperature rise curve
Powerful degreaser is anionic and nonionic surface The compound of active agent and aromatic solvent has high emulsifying, dispersing and dissolving abilities for various mineral oils and vegetable oils, and has good removal ability for silicone softeners and silicon plaque.
For fabrics that do not require color stripping such as downward chromatic aberration and chromatic light deviation discoloration, after clean washing and overflow water washing, oxygen bleaching and chlorine bleaching are not required. It can be washed directly in hot water at 80°C
2.5 Oxygen Bleaching
Oxygen Bleaching Process Conditions
Oxygen bleaching heating curve
After the fabric is stripped, it needs to be oxygenated. Hydrogen peroxide has a strong impurity and decontamination effect. It can effectively remove impurities and oil stains on the fiber, make the fiber obtain a good whiteness, and increase the brightness of the counter-dyed fabric. The pH value of oxygen bleaching working solution is 11~11.5.
2.6 Chlorine bleach
For serious stains and stains Fabrics should be stripped using reducing agents and insurance powder. Sodium hypochlorite should be used for bleaching in areas where local color stains are serious and stripping is difficult.
Chlorine bleaching process conditions
2.7 Dechlorination
After chlorine bleaching, dechlorination must be carried out, otherwise the fabric contains sodium hypochlorite, which will affect the dyeing color. The amount will damage the strength of the fabric and affect the feel.
Dechlorination process conditions
2.8 Secondary dechlorination
The prescription and process parameters of secondary dechlorination are the same as the former. After the second chlorine bleaching, sufficient overflow water washing should be carried out to lay a good foundation for the next step of counter-dying.
2.9 Counterdyeing
Conduct 80℃ on the fabric before counterdyeing X 10 min hot water washing can effectively remove various additives remaining on the fabric and avoid low color yield of dyed fabrics, resulting in secondary replenishment and repair. After the above-mentioned solid removal, silicon removal, color stripping, oxygen bleaching, and chlorine bleaching, the whiteness of the fabric has reached the whiteness before the initial dyeing, and it can be counter-dyed according to the original color number. However, because the fabric has been desolidified, siliconized, stripped, and bleached many times, a very small amount of additives will inevitably remain on the fabric. Therefore, when redying, about 5% more dye should be added simultaneously according to the original dyeing recipe.
Attention
(1) Before solid and silicon removal Washing with hot water at 80°C × 10 rain can effectively remove the softening agent and color-fixing agent on the surface of the fabric that have not reacted with the fibers.
(2) After the fabric is treated at 100°C × 30 minutes to remove solids and silicon, then wash with overflow water to completely remove the softener and solids on the fabric that have not reacted with the fibers. Color agent is used to prevent the softener from demulsifying and oil drifting when peeling at 130°C for 40 minutes.
(3) Because insurance powder is unstable in aqueous solution, it decomposes into sulfur dioxide and releases a lot of heat. When the peeling temperature rises to 80°C, the insurance powder is added cyclically to prevent part of the insurance powder from decomposing and failing during the temperature rise.
(4) Cleaning and oxygen bleaching are carried out after removing solids, silicone and color from the fabric, which can remove residual impurities and oil stains on the fabric and improve the whiteness of the fabric.
(5) For fabrics with serious local color stains and difficult stripping, sodium hypochlorite bleaching is required to remove local pigments on the fabric. Dechlorination must be completed after chlorine bleaching to prevent low color yield of the fabric and damage to the fiber by sodium hypochlorite during counter-dying.
(6) After repeated solid removal, silicon removal, color stripping and bleaching, a very small amount of additives will inevitably remain on the fabric. During re-dying, 5 more additives should be added simultaneously according to the original prescription. About % dye.
Author: Wang Chao, Li Junxing “Repair of defects after finishing pure cotton knitted fabrics” “Printing and Dyeing”
�Unstable, it decomposes into sulfur dioxide and releases a lot of heat. When the peeling temperature rises to 80°C, the insurance powder is added cyclically to prevent part of the insurance powder from decomposing and failing during the temperature rise.
(4) Cleaning and oxygen bleaching are carried out after removing solids, silicone and color from the fabric, which can remove residual impurities and oil stains on the fabric and improve the whiteness of the fabric.
(5) For fabrics with serious local color stains and difficult stripping, sodium hypochlorite bleaching is required to remove local pigments on the fabric. Dechlorination must be completed after chlorine bleaching to prevent low color yield of the fabric and damage to the fiber by sodium hypochlorite during counter-dying.
(6) After repeated solid removal, silicon removal, color stripping and bleaching, a very small amount of additives will inevitably remain on the fabric. During re-dying, 5 more additives should be added simultaneously according to the original prescription. About % dye.
Author: Wang Chao, Li Junxing “Repair of defects after finishing pure cotton knitted fabrics” “Printing and Dyeing”</p






