At present, the control of chemicals in the textile and apparel industry has reached an unprecedentedly strict level, but banned/restricted substances still often exceed standards. So where do these banned/restricted substances come from? Is it caused by printing and dyeing auxiliaries, or is it already present on the gray fabric? Let’s take a look at the banned substances and their sources that may appear in various printing and dyeing processes.
1. Pre-processing
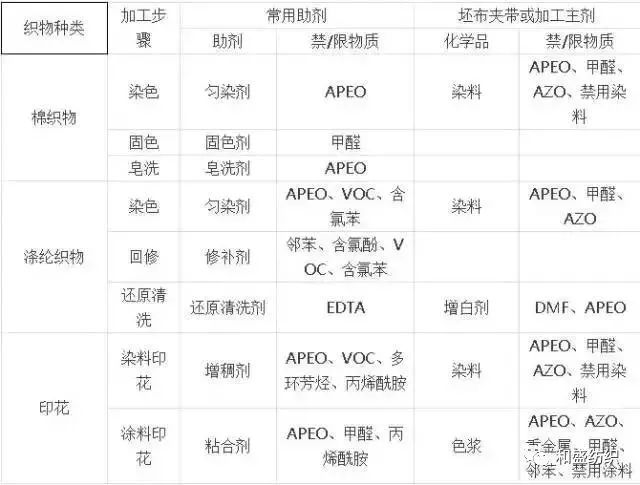
2, dyeing and printing
3. Post-processing
The above analyzes the prohibited and restricted substances that may appear in each process of printing and dyeing. It is worth noting that, Because pre-treatment and dyeing require multiple washings, many toxic and harmful substances are washed away, and only trace amounts remain. However, there is no washing after finishing. Therefore, once the general finishing process additives contain banned substances, it is easy to cause the fabric surface to exceed the standard. .
1 APEO (Alkyl Basic Phenols)
APEO is a type of non-ionic compound, which is what we often call surface Active agents are common ingredients in chemical additives used in the production of clothing and shoe materials. They are widely used as detergents, surfactants or emulsifiers, scouring agents, dye dispersants, printing pastes, spinning oils, and wetting agents. Special attention should be paid to the formulation of chemical dyeing, printing, finishing, cleaning and rinsing of textile and leather auxiliaries. It is used as a dispersant in the manufacturing process of solvent-free synthetic leather. It can also be found in many fibers/yarns/fabrics. Textile lubricants and sizing compounds.
2 pH value
If the various dyes and finishing auxiliaries used in the printing, dyeing and finishing process of textiles have not been Full washing or neutralization, as well as the addition of various finishing agents during the washing process without standardized control, will cause the pH value of the final product to exceed the standard. It is difficult to control the pH value during the production process, because any chemical reagent involved may cause the pH to change, so generally the pH value can be controlled or improved through the final water washing step before leaving the factory. If the pH value of the product is on the high side, it is alkaline. Add some weakly acidic substances such as glacial acetic acid or citric acid during the washing process to achieve the purpose of neutralization; if the pH value of the product is on the low side, which is acidic, add a weakly alkaline substance. Just use baking soda or soap to clean it.
3 Formaldehyde
Formaldehyde found in textiles mainly comes from two aspects. One is the use of formaldehyde-containing finishing The agent is used to make the fabric anti-wrinkle and achieve the effect of no-iron or ironing. This is often found in some shirts that claim to be “no-iron” or “no-iron”. Another reason for failing the formaldehyde test is that glue containing formaldehyde is used on some textiles where accessories are pasted. This is similar to the situation where formaldehyde appears when decorating a house in our internship life. Therefore, if the formaldehyde test fails, the formaldehyde content in the product can be reduced by washing and drying.
4 Azo dyes
Azo dyes are the most widely used synthetic dyes in textile printing and dyeing processes. Dyeing and printing of a wide range of natural and synthetic fibers. Azo dyes themselves are non-toxic and harmless, but under special conditions, they can crack to produce more than 20 aromatic amines that are carcinogenic to the human body. Therefore, what is prohibited in the regulations are azo dyes corresponding to carcinogenic aromatic amines, and the use of all azo dyes is not prohibited. From the analysis of sample data that failed the conventional AZO test, brightly colored fabrics such as red, orange, blue, etc. have a higher probability of failing the AZO test.
5 Phthalates
Phthalates are often called plasticizers. Used to add to plastic to make it soft, increase its elasticity, prevent cracking and make it easier to shape by lowering the melting point of the plastic. However, because its structure is similar to human hormones, it will cause irreparable harm to human sex hormones, especially to children during the growth and development period. According to its main function, it can be known that the materials it is mainly used for include soft plastics, rubber, polymer coatings, printing pastes, synthetic leather, etc. Once banned phthalate is used, it is impossible to improve the phthalate content in the product through post-processing. Only early control can prevent harmful phthalate from entering the production process. But in fact, in addition to phthalates, there are other types of plasticizers that can replace phthalates to achieve the same purpose, such as epoxidized soybean oil, oxalates, etc.
6 Perfluorinated compounds (PFC’s)
The use of perfluorinated compounds on textiles is inseparable from water repellent (DWR) Using technology, DWR treatment is a typical finishing treatment that makes fabrics waterproof, oil-proof and stain-proof, and perfluorinated compounds are also the main components of chemical additives in waterproof and oil-proof finishing treatments. In order to make the fabric waterproof and rainproof, some sportswear and jackets usually use this technology to achieve the ultimate goal. However, some perfluorinated compounds are highly toxic to marine life and cause long-term harmful effects on the marine environment, and excessive or long-term exposure to perfluorinated compounds willIt may damage human fertility and cause harm to the fetus. Therefore, current laws and regulations in various countries, including many NGOs (non-governmental organizations), have become more stringent in their control. However, there is currently no effective substitute for this product on the market, so the purpose of “fluoride removal” can only be achieved by banning its use.
7 Chlorobenzene and chlorophenols
Chlorobenzene is mainly used as an intermediate in the synthesis of other chemicals. Also present as impurities in chemical formulations (such as dyes or pesticides). Chlorobenzene is used as a dye carrier and leveling agent in the dyeing, printing and coating processes of textile and leather raw materials including fibers, yarns and fabrics. They can also be used as deodorizers, fumigants, degreasers and defoliants. Dichlorobenzene is used as a pesticide or as a solvent in rubber, wax or disinfectants. Trichlorobenzene is used as a herbicide, insecticide, or as a solvent in formulations of dyes or other chemicals with higher melting points. Chlorophenols are commonly used as pesticides and textile preservatives. They may also be present as impurities in the raw materials used in dye production. PCP (pentachlorophenol) and TeCP (tetrachlorophenol) can also be used as preservatives in printing pastes.
8 Chlorine-containing organic solvents
Chlorine-containing organic solvents may be used as cleaning solvents or carrier solvents in textile processing. for formulation and functional finishing. They are also used as blowing agents in polyurethane foams and as chemical intermediates in dyes and pesticides, industrial cleaners (e.g., processing equipment, boilers) and stain removers. Pay special attention to chemical formulations used in coated textiles, natural and synthetic leathers, as halogenated solvents are common ingredients. This also includes printing pastes. Consider that halogenated solvents are common carrier solvents in many formulation and functional finishing processes. Industrial cleaners and stain removers used in apparel and footwear production may contain ingredients that are halogenated solvents.
9 Heavy Metals
Heavy metals are a type of substance that everyone is familiar with, and their sources are also widespread. The tap water we use or River water itself contains trace amounts of heavy metals. Trace amounts of heavy metals can play a very important role in the human body as effective mineral elements, but excessive intake of some heavy metals will be deposited in the human body, causing irreparable harm to the human nervous system, endocrine system, etc. In textile processing, the intake of heavy metals is due to the use of some color-related chemicals, such as dyes, pigments, inks, etc., to increase the variety of appearance colors of the product. On the other hand, some accessories, such as those made of metal, plastic, rubber and other materials, themselves contain some heavy metal elements, which may also cause heavy metals to exceed the standard.
10 Organotin Compounds
Organotin was originally used on ships in the navigation industry to protect against marine organisms. Corrosion of hull. Therefore, the main function of organotin chemicals is to be antibacterial, and they are also used in the textile industry. Antibacterial and deodorizing slogans can often be seen on some sports jerseys and sneakers. The main principle is that the fabrics are treated with antibacterial chemical reagents such as organotin. Before the 2006 World Cup in Germany, excessive amounts of organotin compounds were found on the jerseys of a certain country’s football team, which attracted widespread attention around the world.
The restricted substances introduced above are only some of the chemical substances most frequently involved in the textile industry. Of course, the types and scope of substances required by regulations will be wider. As producers and distributors of textiles, only by clearly understanding the source, use and hazards of each chemical substance can we replace and eliminate it from the source, thereby reducing the entry of these harmful chemicals into finished products to meet the requirements of regulations, consumers and society. product requirements. </p







