The active replenishment phase is approaching. At present, the macro atmosphere is warmer, the new crown vaccine is steadily advancing, the economy continues to recover, and domestic export demand and endogenous consumption demand are picking up. From a fundamental point of view, domestic cotton supply is relatively stable, but at the same time there are bullish factors such as a decline in cotton planting intentions and strengthened purchase and storage expectations; the operating conditions of the downstream textile industry have improved, and may enter the active replenishment stage in 2021; domestic terminal clothing consumption demand is expected Maintaining positive growth, foreign trade prosperity continues to rise and export competition pressure is small. Overall, cotton fundamentals continue to improve, the current price is at a relatively low level, and cotton prices will be driven upward in 2021.
The picture shows the continued recovery of the domestic textile market
The picture is domestic The growth rate of cotton yarn exports to Southeast Asia continues to rise
The picture shows that cotton is about to enter the active replenishment stage
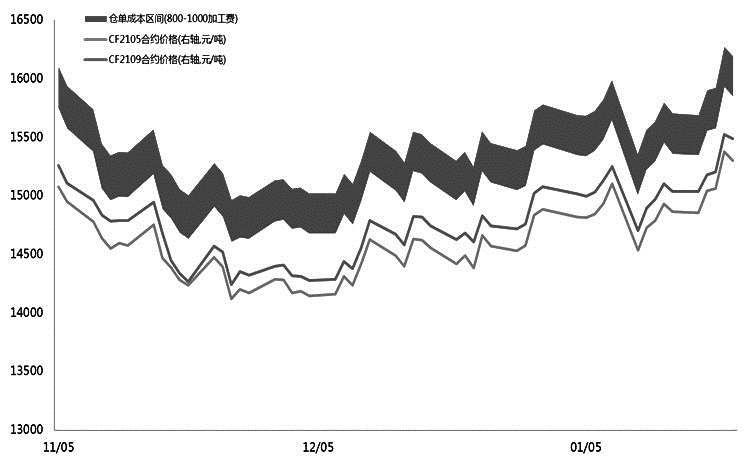
The picture shows the cost range of converted lint from seed cotton
Global macroeconomic policies are loose
The picture shows that the average fiscal deficit rate in the United States was relatively high during the “unity government” period
The increased fiscal stimulus in Europe and the United States is conducive to further recovery of the global economy. European and American central banks launched the largest QE in history from March to October 2020, far exceeding the scale of balance sheet expansion during the 2008 financial crisis, and the statements of European and American central banks on monetary policy were dovish. Since the epidemic, European and American countries have adopted a policy combination of “constant fiscal expansion + sufficient monetary easing” that has become increasingly prominent. If Europe and the United States further increase fiscal stimulus policies in the future, European and American central banks will also need to advance monetary easing policies to coordinate. The first two years of the Biden administration’s first term will completely form a “unity government” situation led by the Democratic Party, which will be conducive to the advancement of Biden’s policies. Judging from the data of all congressional elections and presidential elections from 1965 to the present, the fiscal deficit rate during the “unity government” period will be significantly higher. From the perspective of monetizing the fiscal deficit, fiscal stimulus will be increased and looser policies will be needed. Monetary policy coordination. In addition, the possibility of implementing a larger-scale fiscal stimulus plan related to infrastructure and new energy during Biden’s term has increased, which is conducive to the continuation of “reflation expectations” and supports the rise of asset prices.
The picture shows that the vaccine has basically been promoted in the United States
At present, the global The consumer confidence index in major markets has rebounded, and the purchasing managers index of the cotton textile industry has increased significantly. With the start of the inventory replenishment cycle, the demand effect will further promote the prospects for economic recovery. COVID-19 vaccination is progressing steadily, and subsequent consumption growth expectations continue to increase.
As of the week of January 22, more than 54 million doses of vaccine had been used in 51 countries, according to Bloomberg data. In the United States, according to Bloomberg’s state statistics and data from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the U.S. vaccination program began on December 14 last year, and so far 17.2 million doses have been administered; the new coronavirus vaccine has basically been promoted and used in the United States, with a small number of The state’s vaccination rate is close to 8%. The pace of vaccination in the United States is advancing steadily. If pharmaceutical companies can continue to supply vaccines and the vaccine’s preventive effect remains as expected, new cases in the United States may stop as early as the third quarter of 2021. Generally speaking, although the epidemic in the United Kingdom has worsened, control measures have been relatively strict, and the epidemic in Europe and the United States has peaked and is declining; as vaccination continues to advance, the market expects that post-epidemic consumption will rebound at an accelerated pace, and actual consumer demand will continue to pick up.
The picture shows the rapid rollout of vaccines in the United States
Cotton The overall supply is relatively stable
The table shows the planting intention survey in December 2020 (the total cotton production is expected to decline in 2021/2022)
From the perspective of total supply, total global cotton production is expected to decline in the new year. Judging from the National Cotton Market Monitoring System’s December 2020 survey of China’s intended cotton planting area in 2021, the cotton planting area in the mainland has decreased significantly, mainly because the price ratio between domestic agricultural products and cotton has been at a relatively high level in the past five years. Although the cotton planting area in the northwest inland including Xinjiang is expected to increase, the country’s total cotton output in 2021/2022 is expected to decrease by 1.4% year-on-year.
Internationally, according to an initial survey by the US Cotton Farmers Magazine, the COVID-19 epidemic is expected to have a greater impact on cotton farmers. The intended cotton planting area in the United States in 2021 has been reduced to 11.611 million acres.� Judging from the largest price increases and losses and position fluctuations of major commodity futures before and after the epidemic, prices of agricultural products, black and non-ferrous commodities have all recovered well. Although cotton futures prices have continued to rise by 47% since the epidemic, the increase has been relatively small compared to other varieties. Moderate, in the middle of the main commodity market position. Based on the perspective of cost pricing, cotton prices are expected to rise to more than 17,500 yuan/ton. Cotton supply is relatively stable, and there are also bullish factors such as declining cotton planting intentions and strengthening purchase and storage expectations. The operating conditions of the downstream textile industry have improved and may enter the active replenishment stage in 2021; domestic demand for terminal apparel consumption is expected to maintain positive growth; foreign trade prosperity continues to rise and export competition pressure is small.
The 2020/2021 annual cotton public inspection has come to an end; during the 2020 epidemic blockade stage, due to the negligence of cotton farmers in field management, the new flowers have declined to a certain extent in terms of length, horse value, specific strength and other quality dimensions. , the cost of lint acquisition and processing first fell and then stabilized; although cotton by-products remained at a high level, the high price of seed cotton still led to an increase in the cost of new lint cotton in ginners. The final warehouse receipt cost is theoretically about 15,500 yuan/ton. Based on the cost pricing method, we preset a processing and consumption profit of 10%-15%. Therefore, it is strategically recommended to lay out the far-month CF2109 and CF2201 contracts. The expected price fluctuation range is 17,000-17,800 yuan/ton. Strategically: It is advisable to maintain a long-term thinking, with a target price of 17,500 yuan/ton for the CF2109 contract. Risk factors: COVID-19 vaccine rollout falls short of expectations. </p







