Woven fabric: The fabric formed by two systems (or directions) of yarns that are perpendicular to each other and interlaced according to a certain pattern is called woven fabric (also called woven fabric). The basic organization is the simplest and most basic organization among all types of organizations, and is the basis for various changes and fancy organizations. The basic weaves include plain weave, twill weave and satin weave.
1. Plain weave:Weave parameters Plain weave is the simplest of all fabric weaves. Its organizational rule is one up and down, and the two roots alternate to form a complete organization. —Waterproof Oxford Cloth
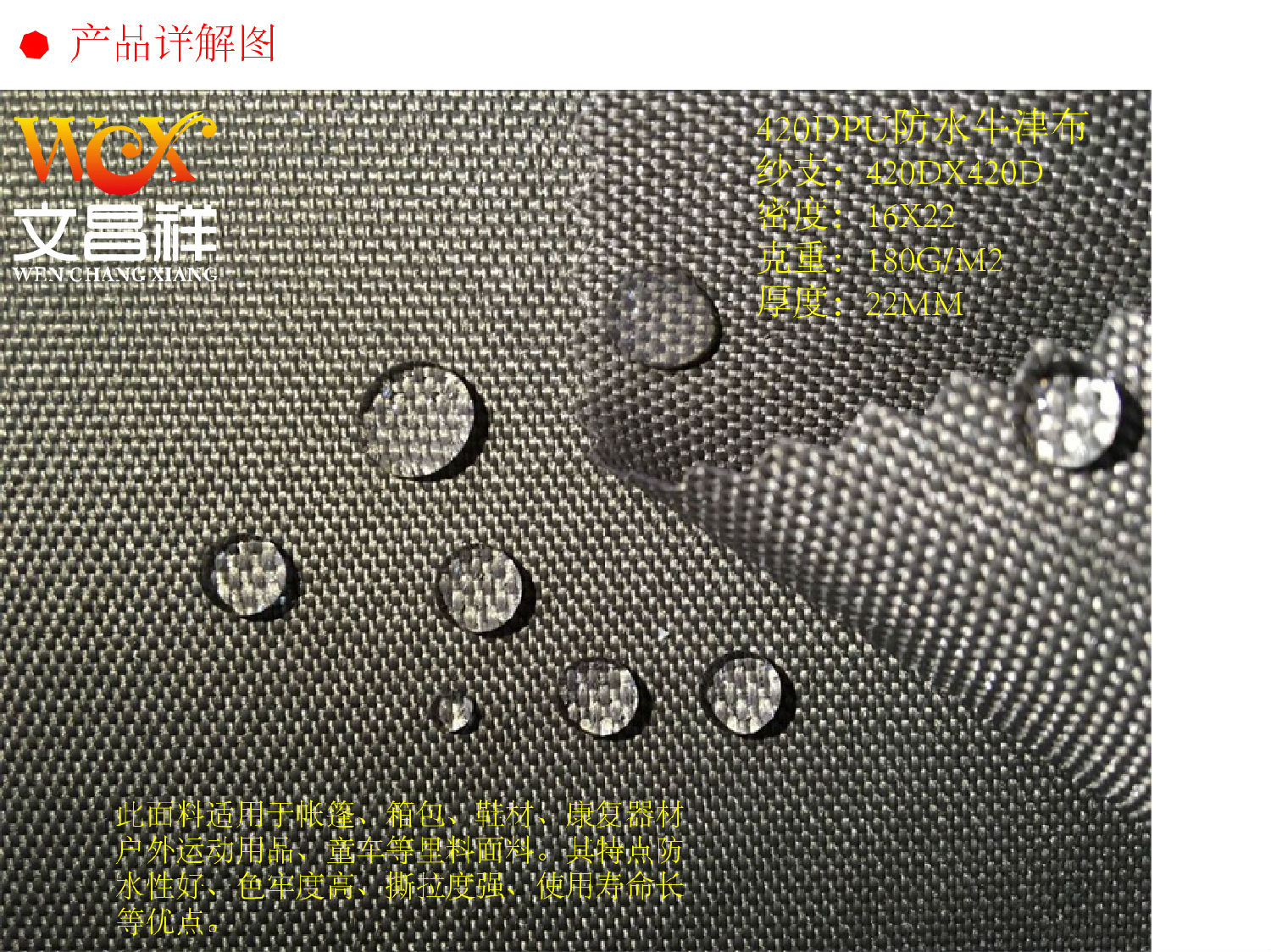
Its characteristics: plain pattern The warp and weft yarns of the organization have the most interlacing points and the yarns buckle a lot, so the fabric surface is flat, the body is stiff, the texture is firm, and the appearance is tight, but the feel is hard and the elasticity is low. In actual use, various methods can be used according to different requirements, such as different thicknesses of warp and weft yarns, changes in warp and weft yarn density, and different combinations and configurations of twist, twist direction and color, etc., to obtain various special products. appearance effect.
Commonly used plain weave fabrics Plain weave fabrics are widely used in cotton, wool, silk, and linen fabrics, such as various plain cloths with smooth surfaces, fine textures Textiles, poplin with clear diamond-shaped particles, grosgrain with obvious concave and convex horizontal stripes, seersucker and georgette with crepe effect, as well as validing, palis, thin tweed, flannel, etc. with hidden grid effect.
2. Twill weave:Twill weave is characterized by short floating lengths in the warp direction or short floating lengths in the weft direction, arranged in a stepped manner, forming a continuous diagonal line on the surface of the fabric. . The movement of each warp yarn in its organization is the same, but the starting point is different. —600D Oxford cloth
Its characteristics: twill weave has warp surface, Weft and double-sided twill. If the surface of the fabric has a majority of warp weave points, such as 2/1, it is a warp twill. On the contrary, if the weft weave points account for a majority, such as 1/3, it is a weft twill. The opposite of warp twill is weft twill, but in the opposite direction. The proportions of the two tissue points on the front and back are the same, but the diagonal directions are opposite, which is called double-sided twill. There are also differences in the degree of inclination of the twill lines. The twill weave uses the intersection angle α between the twill line and the horizontal line to represent the twill inclination angle. As α becomes larger, it means the greater the warp density and the steeper the twill line. The twill when α>450 is called sharp twill, the twill when α<450 is called slow twill, and when α=450, it means that the warp and weft density of the fabric are equal. Twill weave has fewer interweaving points than plain weave and has floating length. Its fabric is softer, thicker and has better gloss than plain weave, but its fastness is not as good as plain weave. The twill lines on its surface can be made clear and obvious according to the choice of twist direction and warp and weft density ratio. Or the texture is plump and prominent, even and straight. —420D Oxford cloth
Common twill fabrics include twill with flat texture, serge, khaki with prominent gongs, gabardine, etc.
3. Satin weave: Tissue parameters and characteristics Satin weave is the most complex of the basic tissues. Its characteristic is that each warp yarn (or weft yarn) has only one single weave point (warp weave point or weft weave point). There is a certain distance between the separate weave points on two adjacent yarns and is separated by two Covered by warp floating threads or weft floating threads, the surface of the fabric is almost entirely composed of a kind of warp floating threads or weft floating threads, so the cloth surface is smooth and even, with good luster and soft texture.
Common satin fabrics Satin weave has a wide range of applications. In cotton and wool fabrics, five-piece satin weaves are mostly used to obtain Zhigong, Henggong, Henggong satin, etc.; in silk fabrics, eight-piece satin weaves are mostly used to obtain various plain satins and floral satins with better luster. Satin or satin patterned fabric.
Suzhou textile bags, tents, strollers, military and other Oxford cloth manufacturers</p






